这篇文章,我们从源码的角度探寻 RocketMQ Producer 的实现机制。
 1 基础配置
1 基础配置我们先展示生产者发送消息的示例代码。
// 1. 初始化默认生产者,传递参数生产者组名DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer(PRODUCER_GROUP);// 2. 设置名字服务地址 producer.setNamesrvAddr("name-server1-ip:9876;name-server2-ip:9876");// 3. 启动生产者服务 producer.start();// 4. 定义消息对象 Message msg = new Message(*TOPIC* /* Topic */, *TAG* /* Tag */, ("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.*DEFAULT_CHARSET*) /* Message body */);msg.setKeys("");// 5. 发送消息// 示例普通消息SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg);// 示例异步回调producer.send(msg, new SendCallback() { @Override public void onSuccess(SendResult sendResult) { // do something } @Override public void onException(Throwable e) { // do something }});// 示例oneway发送producer.sendOneway(msg);发送流程如下:
初始化默认生产者,传递参数生产者组名;设置名字服务地址 ;启动生产者服务;定义消息对象 ;生产者支持普通发送、oneway 发送、异步回调三种方式发送消息 。2 发送消息流程2.1 构造函数下图展示了生产者DefaultMQProducer 类的构造函数,包装类 DefaultMQProducerImpl 是我们这一小节的核心。

构造函数包含两个部分:
初始化实现类 DefaultMQProducerImpl ;根据是否开启消息轨迹参数 enableMsgTrace 判断是否增加消息轨迹逻辑 。2.2 启动生产者DefaultMQProducer 类的 start 方法,本质上是调用包装类 DefaultMQProducerImpl 的 start 方法。

进入 DefaultMQProducerImpl 类,查看该类的逻辑 。
01 检测配置判断生产者组是否合法,生产者名称不能和默认生产者组名称相同。
 02 创建客户端实例
02 创建客户端实例
MQClientInstance 对象通过 MQClientManager 这个单例类创建 ,标志着一个客户端实例,是非常核心的类,每一个实例对象有一个唯一的 clientId。
生产者表/消费者表引用 路由信息03 注册本地生产者boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerProducer(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(), this);
路由信息03 注册本地生产者boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerProducer(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(), this);注册本地生产者的本质是修改客户端实例的生产者表引用:
MQProducerInner prev = this.producerTable.putIfAbsent(group, producer);04 启动客户端实例
实例启动后,会启动通讯模块、定时任务、负载均衡服务、消费者拉取服务。
下图展示了生产者发送消息时,IDEA 里的线程 DUMP 图:

我们需要重点讲讲定时任务 startScheduledTask方法 , 定时任务如下图:

我们重点关注发送心跳和更新路由两个任务。
发送心跳: 定时任务每隔 30 秒将客户端信息发送到 Broker 。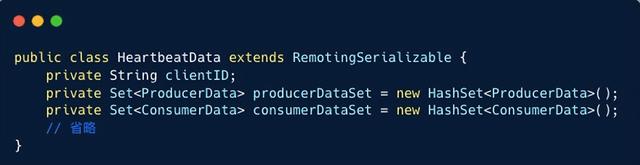
当 Broker 收到心跳请求之后,会通过生产者管理器 ProducerManager、消费者管理器ConsumerManager分别更新生产者客户端缓存、消费者客户端缓存。
更新路由对于生产者来讲,它需要知道需要发送消息的主题对应的路由信息 , 因此需要定时更新路由信息。

更新逻辑比较简单,首先从名字服务获取主题路由信息对象 topicRoute,然后更新 DefaultMQProducerImpl的主题发布信息topicPublishInfoTable对象 。
2.3 发送消息进入 DefaultMQProducerImpl 类,查看发送消息方法 sendDefaultImpl。

笔者将发送消息流程简化如下:
获取主题发布信息;根据路由算法选择一个消息队列,也就是 selectOneMessageQueue方法;调用 sendKernelImpl发放消息对象,封装成发送结果对象 sendResult。01 尝试获取主题发布信息我们知道 MQClientInstance 的定时任务每隔30秒会更新生产者实现类的topicPublishInfoTable,但若第一次发送消息时,若缓存中无数据时候,还是要重新拉取一次。
 02 根据路由算法选择一个消息队列
02 根据路由算法选择一个消息队列RocketMQ 存储模型包含三部分: 数据文件 commitlog 、消费文件 consumequeue 、索引文件 indexfile。
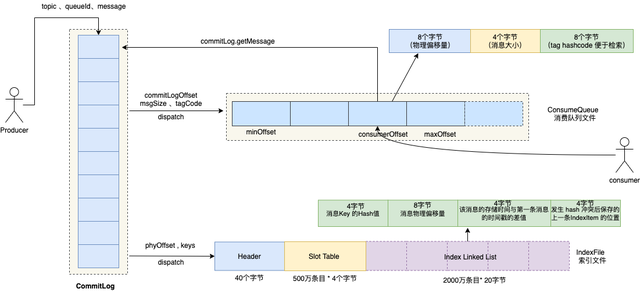

因此根据 RocketMQ 的存储模型设计,对于生产者来讲,发送消息时,必须指定该主题对应的队列。路由算法,我们会在路由机制这一节重点讲解。
MessageQueue mqSelected = this.selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName);03 调用实例客户端 API 发送消息通过路由机制选择一个 messageQueue 之后,调用实例客户端 API 发送消息。

Broker 端在收到发送消息请求后,调用处理器 SendMessageProcessor处理请求,处理完成后,将响应结果返回给生产者客户端,客户端将接收到的数据组装成 SendResult对象。
3 路由机制进入DefaultMQProducerImpl#selectOneMessageQueue 方法:
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) { return this.mqFaultStrategy.selectOneMessageQueue(tpInfo, lastBrokerName);}路由机制通过调用 MQFaultStrategy 的 selectOneMessageQueue 方法 ,这里有一个 sendLatencyFaultEnable 开关变量,默认为 false 。
public MQFaultStrategy { //省略部分代码 日志 private final LatencyFaultTolerance<String> latencyFaultTolerance = new LatencyFaultToleranceImpl(); private boolean sendLatencyFaultEnable = false; private long[] latencyMax = {50L, 100L, 550L, 1000L, 2000L, 3000L, 15000L}; private long[] notAvailableDuration = {0L, 0L, 30000L, 60000L, 120000L, 180000L, 600000L}; //省略部分代码 get/set方法 public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) { // 发送延迟错误策略 if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) { try { int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().incrementAndGet(); for (int i = 0; i < tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); i++) { int pos = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); if (pos < 0) pos = 0; MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(pos); if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName())) return mq; } final String notBestBroker = latencyFaultTolerance.pickOneAtLeast(); int writeQueueNums = tpInfo.getQueueIdByBroker(notBestBroker); if (writeQueueNums > 0) { final MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(); if (notBestBroker != null) { mq.setBrokerName(notBestBroker); mq.setQueueId(tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().incrementAndGet() % writeQueueNums); } return mq; } else { latencyFaultTolerance.remove(notBestBroker); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error("Error occurred when selecting message queue", e); } return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(); } // 默认策略 return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName); } public void updateFaultItem(final String brokerName, final long currentLatency, boolean isolation) { if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) { long duration = computeNotAvailableDuration(isolation ? 30000 : currentLatency); this.latencyFaultTolerance.updateFaultItem(brokerName, currentLatency, duration); } } private long computeNotAvailableDuration(final long currentLatency) { for (int i = latencyMax.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (currentLatency >= latencyMax[i]) return this.notAvailableDuration[i]; } return 0; }}这里有两个逻辑分支 :
sendLatencyFaultEnable 为 false , 通过 TopicPublishInfo 中的 messageQueueList 中选择一个队列(MessageQueue)进行发送消息 ;sendLatencyFaultEnable 为 true ,开启延迟容错机制。3.1 默认机制// TopicPublishInfo 类public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final String lastBrokerName) { if (lastBrokerName == null) { return selectOneMessageQueue(); } else { for (int i = 0; i < this.messageQueueList.size(); i++) { int index = this.sendWhichQueue.incrementAndGet(); int pos = Math.abs(index) % this.messageQueueList.size(); if (pos < 0) pos = 0; MessageQueue mq = this.messageQueueList.get(pos); if (!mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName)) { return mq; } } return selectOneMessageQueue(); }}public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue() { int index = this.sendWhichQueue.incrementAndGet(); int pos = Math.abs(index) % this.messageQueueList.size(); if (pos < 0) pos = 0; return this.messageQueueList.get(pos);}默认机制有两个要点:
循环遍历该主题下所有的队列 ;若上一个失败的 Broker 参数值存在,需要过滤掉上一个失败的 Broker 。3.2 延迟容错机制所谓延迟容错机制,是指发送消息时,若某个队列对应的 Broker 宕机了,在默认机制下很可能下一次选择的队列还是在已经宕机的 broker ,没有办法规避故障的broker,因此消息发送很可能会再次失败,重试发送造成了不必要的性能损失。
因此 producer 提供了延迟容错机制来规避故障的 Broker 。
当sendLatencyFaultEnable 开关为 true 时,在随机递增取模的基础上,代码逻辑会再去过滤掉 not available 的 Broker 。
if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName())) return mq;所谓的" latencyFaultTolerance ",是指对之前失败的,按一定的时间做退避。
例如,如果上次请求的latency超过 550Lms,就退避 3000Lms;超过1000L,就退避 60000L ;如果关闭,采用随机递增取模的方式选择一个队列(MessageQueue)来发送消息,latencyFaultTolerance 机制是实现消息发送高可用的核心关键所在。
sendResult = this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout - costTime);endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false);发送消息时捕捉到异常同样会调用 updateFaultItem 方法:
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, true);endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev等于消息发送耗时,如果成功发送第三个参数传的是 false ,发送失败传 true。
继续查看 MQFaultStrategy#updateFaultItem 源码:
public void updateFaultItem(final String brokerName, final long currentLatency, boolean isolation) { if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) { long duration = computeNotAvailableDuration(isolation ? 30000 : currentLatency); this.latencyFaultTolerance.updateFaultItem(brokerName, currentLatency, duration); }}private long computeNotAvailableDuration(final long currentLatency) { for (int i = latencyMax.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (currentLatency >= latencyMax[i]) return this.notAvailableDuration[i]; } return 0;}computeNotAvailableDuration方法会判断当前消息发送耗时,位于哪一个延迟级别,然后选择对应的 duration 。
private long[] latencyMax = {50L, 100L, 550L, 1000L, 2000L, 3000L, 15000L};private long[] notAvailableDuration = {0L, 0L, 30000L, 60000L, 120000L, 180000L, 600000L};如果isolation 为 true,该 broker 会得到一个10分钟规避时长 ,也就是 600000L 毫秒 。
如果 isolation 为 false,假设 currentLatency 为 600L , 那么规避时间 30000L 毫秒。
查看 LatencyFaultToleranceImpl#updateFaultItem 源码:
public void updateFaultItem(final String name, final long currentLatency, final long notAvailableDuration) { // 从缓存中获取失败条目 FaultItem old = this.faultItemTable.get(name); if (null == old) { //若缓存中没有,则创建 final FaultItem faultItem = new FaultItem(name); faultItem.setCurrentLatency(currentLatency); // broker的开始可用时间=当前时间+规避时长 faultItem.setStartTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis() + notAvailableDuration); old = this.faultItemTable.putIfAbsent(name, faultItem); if (old != null) { old.setCurrentLatency(currentLatency); old.setStartTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis() + notAvailableDuration); } } else { // 更新旧的失败条目 old.setCurrentLatency(currentLatency); old.setStartTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis() + notAvailableDuration); }}FaultItem 为存储故障 broker 的类,称为失败条目,每个条目存储了 broker 的名称、消息发送延迟时长、故障规避开始时间。
该方法主要是对失败条目的一些更新操作,如果失败条目已存在,那么更新失败条目,如果失败条目不存在,那么新建失败条目,其中失败条目的startTimestamp为当前系统时间加上规避时长,startTimestamp 是判断 broker 是否可用的时间值:
public boolean isAvailable() { return (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTimestamp) >= 0;}4 顺序消息顺序消息可以保证消息的消费顺序和发送的顺序一致,即先发送的先消费,后发送的后消费,常用于金融证券、电商业务等对消息指令顺序有严格要求的场景。
4.1 如何保证顺序消息消息的顺序需要由以下三个阶段保证:
消息发送如上图所示,A1、B1、A2、A3、B2、B3 是订单 A 和订单 B 的消息产生的顺序,业务上要求同一订单的消息保持顺序,例如订单A的消息发送和消费都按照 A1、A2、A3 的顺序。如果是普通消息,订单A的消息可能会被轮询发送到不同的队列中,不同队列的消息将无法保持顺序,而顺序消息发送时 RocketMQ 支持将 Sharding Key 相同(例如同一订单号)的消息序路由到一个队列中。RocketMQ 版服务端判定消息产生的顺序性是参照同一生产者发送消息的时序。不同生产者、不同线程并发产生的消息,云消息队列 RocketMQ 版服务端无法判定消息的先后顺序。消息存储顺序消息的 Topic 中,每个逻辑队列对应一个物理队列,当消息按照顺序发送到 Topic 中的逻辑队列时,每个分区的消息将按照同样的顺序存储到对应的物理队列中。对于 kafka 来讲,1个主题会有多个分区,数据存储在每个分区,分区里文件以 Segment 文件串联起来。对于 RocketMQ 来讲 , 存储模型包含三部分: 数据文件 commitlog 、消费文件 consumequeue 、索引文件 indexfile。kafka 和 RocketMQ 文件模型很类似,只不过 kafka 的文件数据都会存储在不同的分区里,而 RocketMQ 的数据都存储在 CommitLog 文件里 ,不同的消息会存储在不同的消费队列文件里,便于提升消费者性能(索引)。所以我们只需要将特定的消息发送到特定的逻辑队列里,对于 kafka 来讲是分区 partition ,对于 RocketMQ 来讲,就是消费队列 messageQueue 。消息消费RocketMQ 按照存储的顺序将消息投递给 Consumer,Consumer 收到消息后也不对消息顺序做任何处理,按照接收到的顺序进行消费。Consumer 消费消息时,同一 Sharding Key 的消息使用单线程消费,保证消息消费顺序和存储顺序一致,最终实现消费顺序和发布顺序的一致。4.2. 生产者发送顺序消息下面的代码展示生产者如何发生顺序消息 。
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("please_rename_unique_group_name");producer.start(); String[] tags = new String[] {"TagA", "TagB", "TagC", "TagD", "TagE"}; for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { int orderId = i % 10; Message msg = new Message("TopicTestjjj", tags[i % tags.length], "KEY" + i, ("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET)); SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg, new MessageQueueSelector() { @Override public MessageQueue select(List<MessageQueue> mqs, Message msg, Object arg) { Integer id = (Integer) arg; int index = id % mqs.size(); return mqs.get(index); } }, orderId); System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);}producer.shutdown();发送顺序消息需要定制队列选择器 MessageQueueSelector。
SendResult send(final Message msg, final MessageQueueSelector selector, final Object arg) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException;public interface MessageQueueSelector { MessageQueue select(final List<MessageQueue> mqs, final Message msg, final Object arg);}进入 DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendSelectImpl, 查看顺序消费发送的实现逻辑。
private SendResult sendSelectImpl( Message msg, MessageQueueSelector selector, Object arg, final CommunicationMode communicationMode, final SendCallback sendCallback, final long timeout ) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException { // 省略代码 TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic()); if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) { MessageQueue mq = null; try { List<MessageQueue> messageQueueList = mQClientFactory.getMQAdminImpl().parsePublishMessageQueues(topicPublishInfo.getMessageQueueList()); Message userMessage = MessageAccessor.cloneMessage(msg); String userTopic = NamespaceUtil.withoutNamespace(userMessage.getTopic(), mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().getNamespace()); userMessage.setTopic(userTopic); // 调用 selector 的select 方法,传递相关参数,选择某一个队列 mq = mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().queueWithNamespace(selector.select(messageQueueList, userMessage, arg)); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new MQClientException("select message queue threw exception.", e); } long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime; if (timeout < costTime) { throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendSelectImpl call timeout"); } if (mq != null) { return this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, null, timeout - costTime); } else { throw new MQClientException("select message queue return null.", null); } } validateNameServerSetting(); throw new MQClientException("No route info for this topic, " + msg.getTopic(), null);}从上面的顺序消息发送代码,我们得到两点结论:
顺序消息发送时,需要实现 MessageQueueSelector 的 select方法 ;发送顺序消息时,若发送失败没有重试。参考文档:
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/918025
